The clothing manufacturing process involves a series of carefully managed steps that turn raw materials into finished garments. From design and sourcing to production and delivery, find out in this article how each stage works together to ensure quality and efficiency.
What is the manufacturing process of clothes?
Clothing manufacturing is the journey that turns an idea into a finished garment ready to be worn. From early design choices to final delivery, each stage plays a role in making sure the product looks right, fits well, and meets quality standards. Understanding this process helps brands, designers, and even new business owners see how the clothing manufacturing process works in real life.
At its core, clothing manufacturing covers all the operations needed to produce garments at scale. This includes cutting fabric, sewing pieces together, and finishing each item with labels, tags, and final checks. The full process is usually broken down into smaller steps, known as sub-operations, which can vary depending on the type of garment, the machinery used, and the skills of the workforce.
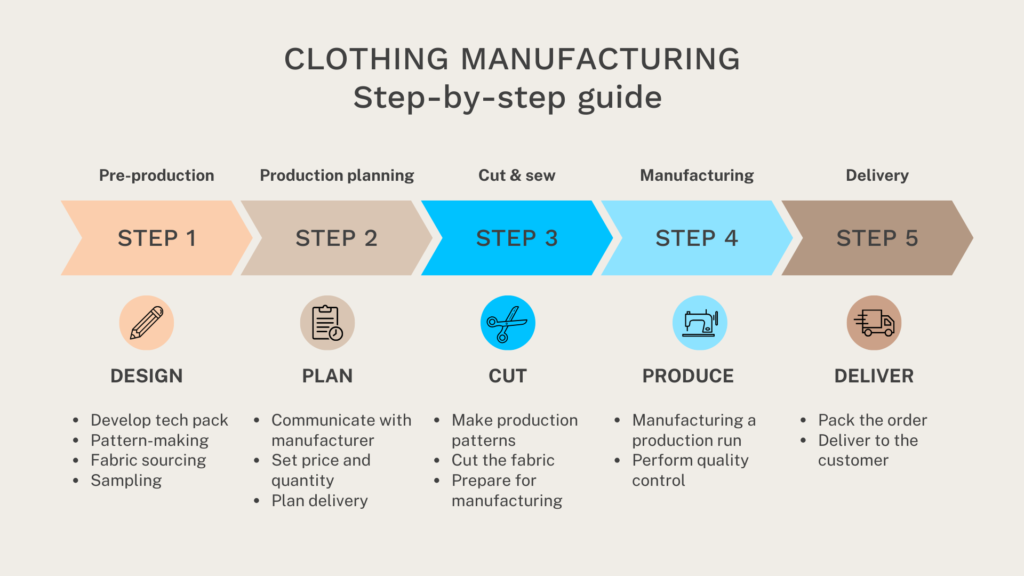
The clothing manufacturing business follows a structured workflow to keep production efficient and consistent. While details may differ between factories, most manufacturers follow a similar step by step approach.
1. Pre-Production & Design
Pre-production and design set the foundation for the entire clothing manufacturing process. This stage focuses on turning creative ideas into clear, workable instructions that factories can follow accurately and consistently.
Design development
Everything starts with design development. Brands and designers research trends, define the target market, and create initial sketches based on style, function, and season. These ideas are then translated into technical drawings and tech packs, which include measurements, materials, construction details, and finishing instructions. A clear tech pack helps avoid misunderstandings later in production.

Material sourcing
Once the design is confirmed, the next step is material sourcing. This involves selecting and purchasing fabrics, threads, zippers, buttons, and trims that match the design and quality requirements. Factors such as cost, availability, durability, and lead time are carefully considered, as material choices directly affect the final garment and production schedule.
Pattern making and grading
Pattern making turns the design into physical or digital templates for each garment piece. These patterns act as a blueprint for cutting fabric. After the base pattern is created, it is graded into different sizes to ensure consistent fit across the size range. Accurate patterns are essential, as even small errors can lead to fitting issues during mass production.

Sampling and approval
Sampling is the final step in pre-production. Prototype garments are produced to test fit, construction, and overall appearance. These samples are reviewed, adjusted if needed, and approved before bulk production begins. This stage allows brands to spot potential issues early and make changes without costly delays later on.
With designs finalised, materials sourced, and samples approved, the project is ready to move forward. The next step is Production, where plans are put into action and garments begin to take shape at scale.
2. Production
The production stage is where designs move from planning to reality. At this point, approved patterns, materials, and samples are used to manufacture garments in larger quantities, following a structured and efficient workflow.
Fabric spreading and cutting
Production begins with fabric spreading and cutting. Fabric is laid out in multiple layers on large cutting tables to ensure consistency across all pieces. Using the approved patterns, the fabric is then cut with high precision. Many modern clothing manufacturers rely on automated or computer-controlled cutting machines to improve accuracy, speed up production, and reduce fabric waste.
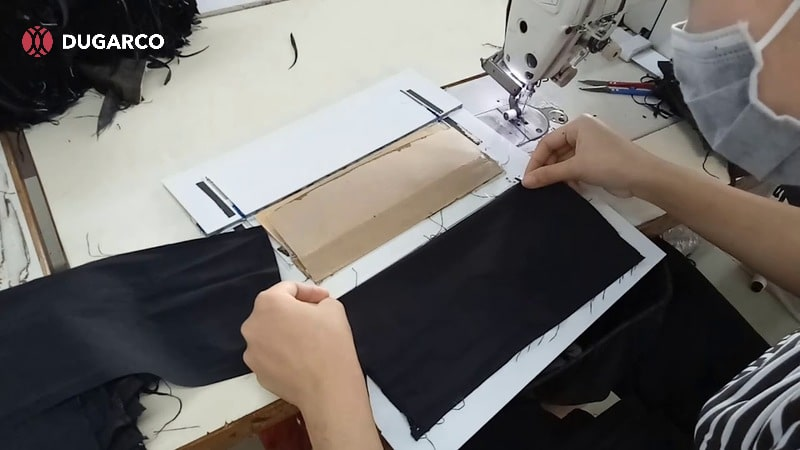

Sewing and assembly
Once the fabric pieces are cut, they move to sewing and assembly. Here, individual components are stitched together on industrial sewing machines, often organised in assembly lines. Each workstation handles a specific task, such as attaching sleeves or sewing seams, which helps maintain quality and efficiency throughout the clothing manufacturing process.
Embellishments and treatments
After basic assembly, garments may go through embellishment processes. This can include printing, embroidery, dyeing, washing, or other decorative techniques that add visual detail and character to the clothing. These steps are carefully controlled to ensure colours, placement, and finishes match the original design.
Finishing touches
The final part of production is finishing. Loose threads are trimmed, garments are pressed or ironed to achieve the correct shape, and labels and tags are added. These details ensure each item looks polished and ready for inspection.
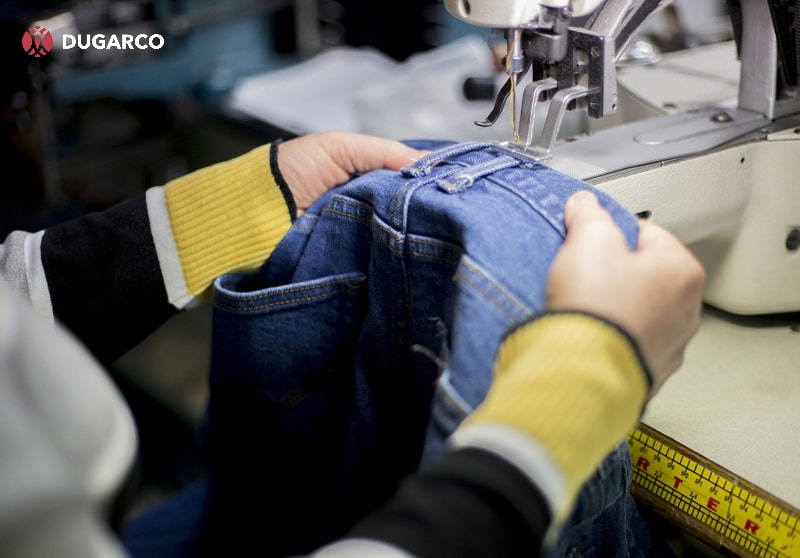

Once production is complete, garments move into the Post-Production stage, where quality control and preparation for delivery ensure the finished products meet the required standards before reaching customers.
3. Post-Production
Post-production is the final stage of the clothing manufacturing process, ensuring that finished garments meet quality expectations and are ready for delivery. This phase focuses on inspection, packaging, and distribution, helping brands protect their products and reputation before items reach the market.
Quality control (QC)
Quality control is carried out once production is complete. Each garment is inspected for fabric defects, stitching issues, colour consistency, and correct sizing. Measurements are checked against the approved size chart, and overall appearance is reviewed to ensure the garment matches the original design and sample. Any items that fail to meet the required standards are repaired, reworked, or removed before approval.
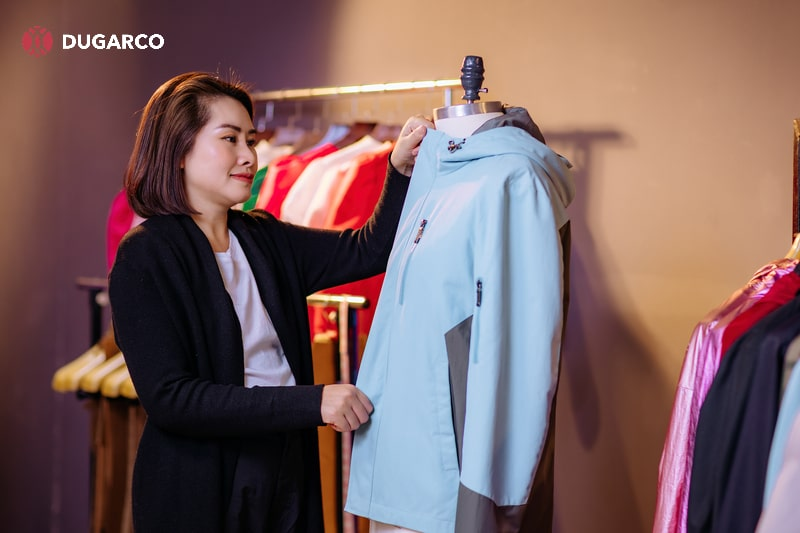

Packaging and distribution
After passing quality control, garments move on to packaging and distribution. Items are folded neatly, tagged, and packed into protective bags before being boxed for shipment. Packaging is often customized to meet brand or retailer requirements. Once prepared, the garments are shipped to retailers, warehouses, or directly to customers, completing the manufacturing cycle.
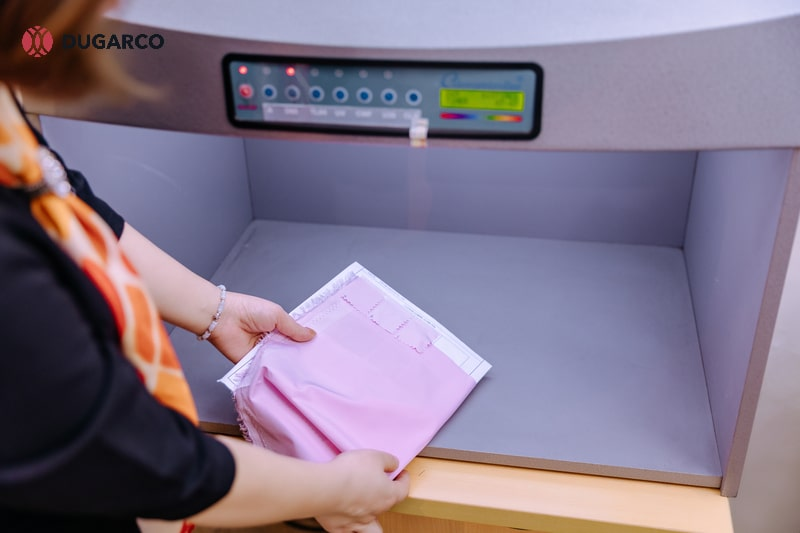

With post-production finished, the clothing manufacturing process comes full circle, from initial design to final delivery, ready for garments to enter the market and reach end consumers.
Understanding the clothing manufacturing process helps brands and businesses manage production more effectively and avoid costly mistakes. By following each stage carefully, from pre-production to post-production, garments can be produced to a high standard and delivered ready for the market.

Dugarco under the talented leadership and guidance of Mr. Hoang Ve Dung has gradually become a large Vietnam clothing manufacturer, supplying clothes for many famous brands from many different countries such as the UK, USA, and Australia.





